트리(Tree) 개념 및 구현
Intro
이 글은 트리(Tree) 자료구조의 개념과 특징 그리고 구현에 대한 정보를 담은 글입니다.
트리 개념 및 특징

트리의 개념: 트리는 노드가 나뭇가지처럼 연결된 비선형 계층적 자료구조이다.
트리 구조는 운영체제의 파일 시스템이나 HTML을 사용할 때 다루는 DOM에 활용된다.
- 트리의 구성 요소: 뿌리, 가지, 잎
- 부모, 자식, 형제 노드
ex. A와 B,C: A는 부모 노드, B와 C는 자식 노드, B와 C는 서로 형제 노드
- 경로, 길이, 깊이, 레벨, 높이, 차수
경로는 출발 노드에서 목적 노드까지 거쳐야 하는 노드
길이는 출발 노드에서 목적 노드까지 거쳐야 하는 노드의 개수
깊이는 뿌리 노드에서 해당 노드까지 이르는 경로의 길이
레벨은 깊이가 같은 노드의 집합
높이는 가장 깊은 곳에 있는 잎 노드까지의 길이
노드의 차수는 그 노드의 자식 노드 개수
트리의 차수는 트리 내에 있는 노드 중에서 가장 자식이 많은 노드의 차수
트리 표현 방법
- 중첩된 괄호 표현법
ex. (1(2(3)(4))(5(6)(7)))
- 중첩된 집합 표현법
.png?type=w800)
- 들여쓰기 표현법
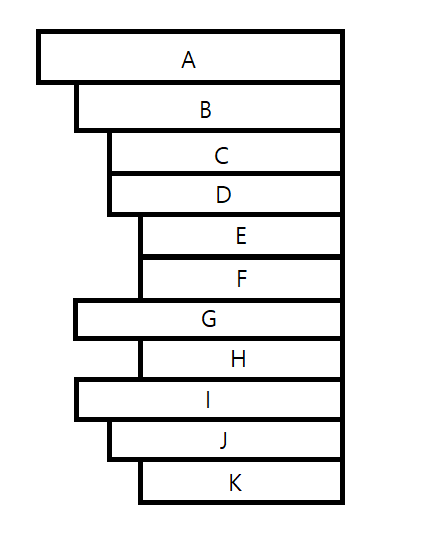
노드 표현 방법
- N-link 표현법

- left child right sibling 표현법

트리 구현에 필요한 연산
1. 노드 생성/소멸 연산
2. 자식 노드 연결 연산
3. 트리 출력 연산
4. 트리 소멸 연산
1. 노드 선언
// 노드선언
typedef struct tagNode{
struct tagNode* Leftchild; //왼쪽에는 자식 노드
struct tagNode* RightSibling; // 오른쪽에는 형제 노드
int data;
} Node;
노드 선언을 하는 부분은 기존에 작성하는 것과 비슷하다.
왼쪽에는 자식노드, 오른쪽에는 형제노드를 연결 하기 위한 포인터를 선언하고
각 노드마다 들어갈 데이터 변수를 선언한다.
2. 노드 생성/소멸 연산
// 노드 생성-소멸 연산
Node* createNode(int newdata){
Node* NewNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
NewNode->Leftchild = NULL; // 초기화
NewNode->RightSibling = NULL;
NewNode->data = newdata; // newdata 대입
return NewNode;
}
void destroyNode(Node* _Node){
free(_Node);
}
노드를 생성하는 부분도 앞에서 한 부분과 유사하다.
malloc을 통한 메모리 할당을 해 주고, 자식노드와 형제노드를 위한 포인터도 NULL로 초기화 해준다.
그리고 노드의 data에 newdata를 할당하고 NewNode를 반환한다.
노드 소멸은 free를 통한 메모리 해제로 실행한다.
3. 자식 노드 연결(Add_ChildNode) 연산
// 자식 노드 연결
void Add_ChildNode(Node* Parent, Node* Child){
if (Parent->Leftchild == NULL){
Parent->Leftchild = Child;
}
else{
Node* Temp = Parent->Leftchild;
while(Temp->RightSibling != NULL)
Temp = Temp->RightSibling;
Temp->RightSibling = Child;
}
}
자식 노드 연결 연산은 한 노드와 자식 노드 간의 연결을 해주는 연산을 말한다.
만약에 부모 노드에 자식 노드가 없으면 바로 부모 노드가 지시하는 자식 노드에 새 자식 노드를 연결한다.
만약 기존에 자식 노드가 있다면, Temp에 자식 노드 포인터를 할당한 후에 그 노드의 형제 노드가 NULL이 될 때까지 반복문을 실행해서
형제 노드의 끝에 새 노드를 추가한다.
4. 트리 출력 연산
// 트리 출력
void PrintTree(Node* _Node, int depth){
// 들여쓰기
for (int i = 0; i < depth-1; i++){
printf(" ");
}
if (depth > 0) // 자식 노드 여부 표시
printf("+--");
// 노드 데이터 출력
printf("%d\n", _Node->data);
if (_Node->Leftchild != NULL){
PrintTree(_Node->Leftchild, depth+1);
}
if (_Node->RightSibling != NULL){
PrintTree(_Node->RightSibling, depth);
}
}
트리에 있는 노드 출력을 들여쓰기 표현법으로 출력하는 함수이다.
먼저 들여쓰기를 출력한 다음에(제일 위의 부모 노드는 depth가 0이기 때문에 반복문 수행 안 함),
만약 depth가 0보다 크다면 “+–“를 출력해서 자식 노드임을 보여준다. 그리고 노드의 data를 출력한다.
만약 노드의 자식 노드가 NULL이 아니라면, PrintTree()를 재귀 호출하여 다시 실행하고,
만약 노드의 형제 노드가 NULL이 아니라도 ,PrintTree()를 재귀 호출해서 다시 실행한다.
자식 노드가 있을 때 조건문에서 depth+1을 하는 이유는 depth가 0인 상태에서 점점 아래로 내려가야 하기 때문이고,
형제 노드가 있을 때 조건문에서 depth가 그대로인 이유는 형제 노드는 이미 내려간 자식 노드와 같은 계층이기 때문이다.
5. 트리 소멸 연산
// 트리 소멸
void destroyTree(Node* Root){
if (Root->RightSibling != NULL) // Root에 형제 노드가 있으면
destroyTree(Root->RightSibling); // 형제 노드 지우기(재귀)
if (Root->Leftchild != NULL) // 자식 노드가 있으면
destroyTree(Root->Leftchild); // 자식 노드 지우기(재귀)
Root->Leftchild = NULL; // 형제 노드 없으면 형제 노드 NULL로 초기화
Root->RightSibling = NULL; // 자식 노드 없으면 자식 노드 NULL로 초기화
destroyNode(Root); // 루트 노드 지우기
}
트리 소멸은 먼저 자식 노드가 있거나 형제 노드가 있을 때, 그 노드부터 지우는 방식으로 제거가 이루어져야 한다.
노드 제거는 함수를 재귀 호출하는 방식으로 진행된다.
그리고 자식 노드와 형제 노드의 제거가 완료되면 루트 노드의 제거를 진행한다.
전체 구현 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 노드선언
typedef struct tagNode{
struct tagNode* Leftchild; //왼쪽에는 자식 노드
struct tagNode* RightSibling; // 오른쪽에는 형제 노드
int data;
} Node;
// 노드 생성-소멸 연산
Node* createNode(int newdata){
Node* NewNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
NewNode->Leftchild = NULL; // 초기화
NewNode->RightSibling = NULL;
NewNode->data = newdata; // newdata 대입
return NewNode;
}
void destroyNode(Node* _Node){
free(_Node);
}
// 트리 소멸
void destroyTree(Node* Root){
if (Root->RightSibling != NULL) // Root에 형제 노드가 있으면
destroyTree(Root->RightSibling); // 형제 노드 지우기(재귀)
if (Root->Leftchild != NULL) // 자식 노드가 있으면
destroyTree(Root->Leftchild); // 자식 노드 지우기(재귀)
Root->Leftchild = NULL; // 형제 노드 없으면 형제 노드 NULL로 초기화
Root->RightSibling = NULL; // 자식 노드 없으면 자식 노드 NULL로 초기화
destroyNode(Root); // 루트 노드 지우기
}
// 자식 노드 연결
void Add_ChildNode(Node* Parent, Node* Child){
if (Parent->Leftchild == NULL){
Parent->Leftchild = Child;
}
else{
Node* Temp = Parent->Leftchild;
while(Temp->RightSibling != NULL)
Temp = Temp->RightSibling;
Temp->RightSibling = Child;
}
}
// 트리 출력
void PrintTree(Node* _Node, int depth){
// 들여쓰기
for (int i = 0; i < depth-1; i++){
printf(" ");
}
if (depth > 0) // 자식 노드 여부 표시
printf("+--");
// 노드 데이터 출력
printf("%d\n", _Node->data);
if (_Node->Leftchild != NULL){
PrintTree(_Node->Leftchild, depth+1);
}
if (_Node->RightSibling != NULL){
PrintTree(_Node->RightSibling, depth);
}
}
int main(void){
Node* Root = createNode(1);
Node* Node2 = createNode(2);
Node* Node3 = createNode(3);
Node* Node4 = createNode(4);
Node* Node5 = createNode(5);
Node* Node6 = createNode(6);
Node* Node7 = createNode(7);
Add_ChildNode(Root, Node2);
Add_ChildNode(Node2, Node3);
Add_ChildNode(Node2, Node4);
Add_ChildNode(Root, Node5);
Add_ChildNode(Node5, Node6);
Add_ChildNode(Node5, Node7);
PrintTree(Root, 0);
destroyTree(Root);
}
출력 결과
1
+–2
+–3
+–4
+–5
+–6
+–7


댓글남기기